Scanning sensors
A training session uses a sensor to obtain Heart rate data. Rook Training SDK supports all BLE sensors that use the Heart Rate Profile.
In this tutorial you will learn how to:
- Scan sensors.
- Link sensors to a user.
- Save a sensor in preferences.
You will code an Activity to scan sensors and display them in a list, when the user selects one it will be linked and the MAC will be added to the result of the Activity.
This tutorial is the second part of a Individual training.
Contents
- The UI
- The Repositories
- RMSensorScanner
- The ViewModels
- Integrate ViewModel and UI
- Running the app
- Next steps
Coding the UI
This section covers 2 activities:
- HomeActivity - The home UI of the app.
- SensorScannerActivity - Will display a list of sensors.
The file structure should look like below:
your.package.name/
|-- ui/
|-- home/
|-- HomeActivity
|-- scanner/
|-- adapter/
|-- BLPeripheralAdapter
|-- BLPeripheralDiff
|-- ScannerKeys
|-- SensorScannerActivity
Create the UI for each activity.
The activity_home.xml file will show a "Sensor scanner" button.
<!-- Other buttons -->
<com.google.android.material.button.MaterialButton
android:id="@+id/sensor_scanner"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginBottom="10dp"
android:text="@string/sensor_scanner" />
</LinearLayout>
</ScrollView>
The activity_sensor_scanner.xml file will show the sensors list
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:paddingHorizontal="20dp"
android:paddingTop="20dp"
tools:context=".ui.scanner.SensorScannerActivity">
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginBottom="20dp"
android:text="@string/sensor_scanner"
android:textAlignment="center"
android:textAppearance="@style/TextAppearance.MaterialComponents.Headline6"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/connected_sensor"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginBottom="10dp"
android:drawablePadding="10dp"
android:gravity="center_vertical"
android:text="@string/connected_to_placeholder"
android:textAppearance="@style/TextAppearance.MaterialComponents.Body1"
android:visibility="gone"
app:drawableEndCompat="@drawable/ic_bluetooth_connected"
app:drawableTint="?attr/colorControlNormal"/>
<include
android:id="@+id/progress"
layout="@layout/ui_progress"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"/>
<androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView
android:id="@+id/data"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:visibility="gone"
app:layoutManager="androidx.recyclerview.widget.LinearLayoutManager"
tools:listitem="@layout/list_tile_sensor"/>
</LinearLayout>
The list_tile_sensor.xml along with its adapter and diff which represents a sensor item.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<com.google.android.material.card.MaterialCardView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:cardCornerRadius="5dp"
app:cardElevation="5dp"
app:cardUseCompatPadding="true">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:gravity="center_vertical"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:paddingHorizontal="10dp"
android:paddingVertical="10dp"
tools:ignore="UseCompoundDrawables">
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/icon"
android:layout_width="40dp"
android:layout_height="40dp"
android:contentDescription="@null"
android:src="@drawable/ic_sensor"
app:tint="?attr/colorControlNormal"/>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginHorizontal="10dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/name"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginBottom="10dp"
android:textAppearance="@style/TextAppearance.MaterialComponents.Body1"
tools:text="RookC2"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/connect_message"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/touch_to_connect"
android:textAppearance="@style/TextAppearance.MaterialComponents.Caption"
android:textColor="@color/black"/>
</LinearLayout>
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/icon_bluetooth"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:contentDescription="@null"
android:src="@drawable/ic_bluetooth"
app:tint="?attr/colorControlNormal"/>
</LinearLayout>
</com.google.android.material.card.MaterialCardView>
class BLPeripheralAdapter(
private val onClick: (BluetoothPeripheral) -> Unit
) : ListAdapter<BluetoothPeripheral, BLPeripheralAdapter.ViewHolder>(BLPeripheralDiff()) {
inner class ViewHolder(private val binding: ListTileSensorBinding) :
RecyclerView.ViewHolder(binding.root) {
fun bind(peripheral: BluetoothPeripheral) {
val context = binding.root.context
with(binding) {
name.text = peripheral.name ?: context.getString(R.string.unknown_sensor)
root.setOnClickListener { onClick(peripheral) }
}
}
}
override fun onCreateViewHolder(parent: ViewGroup, viewType: Int): ViewHolder {
return ViewHolder(
ListTileSensorBinding.inflate(LayoutInflater.from(parent.context), parent, false)
)
}
override fun onBindViewHolder(holder: ViewHolder, position: Int) {
holder.bind(getItem(position))
}
}
class BLPeripheralDiff : DiffUtil.ItemCallback<BluetoothPeripheral>() {
override fun areItemsTheSame(old: BluetoothPeripheral, new: BluetoothPeripheral): Boolean {
return old.address == new.address
}
override fun areContentsTheSame(old: BluetoothPeripheral, new: BluetoothPeripheral): Boolean {
return old.address == new.address &&
old.name == new.name
}
}
The ScannerKeys has constants that will be used to pass parameters from HomeActivity
to SensorScannerActivity and vice versa.
package com.rookmotion.rooktraining.ui.scanner
object ScannerKeys {
const val SENSOR_SELECTED = "sensor_selected"
const val SENSOR_CONNECTED_MAC = "sensor_connected_mac"
const val SENSOR_CONNECTED_NAME = "sensor_connected_name"
}
Finally, go to your.package.name/utils/RMExtensions and create an extension function to show a SnackBar.
fun View.snackLong(message: String, action: String, onClick: () -> Unit) {
Snackbar.make(
this,
message,
Snackbar.LENGTH_LONG
).setAction(action) { onClick() }.show()
}
Coding the repositories
The file structure should look like below:
your.package.name/
|-- data/
|-- repository/
|-- SensorRepository
Create an SensorRepository class with an RM instance as a constructor parameter.
package com.rookmotion.rooktraining.data.repository
import com.rookmotion.app.sdk.RM
class SensorRepository(private val rm: RM) {
}
To get all sensors linked to the user call getSensors, this function will attempt to fetch the Api, then save the
response in Database a return it. If the Api request fails it will return whatever is stored in Database.
There's also a getSensorsFromDatabase function if you only want to get local sensors.
fun getSensors(
onSuccess: (List<RMSensor>) -> Unit,
onError: (String) -> Unit
) {
rm.getSensors { rmResponse, result ->
if (rmResponse.isSuccess && result != null) {
onSuccess(result)
} else {
onError(rmResponse.message)
}
}
}
To link (save) a sensor to the user call saveSensorFromBluetoothPeripheral this function will create a relation
between the sensor and the user UUID and then return a sensor UUID in a RMSensor object if that relation already exits
it will return the same RMSensor object and a 409 in the RMResponse code.
Additionally, if the above process succeeds the RMSensor object will also be stored in the Database.
fun saveSensor(
peripheral: BluetoothPeripheral,
onSuccess: (RMSensor) -> Unit,
onError: (String) -> Unit
) {
rm.saveSensorFromBluetoothPeripheral(peripheral) { rmResponse, result ->
if (rmResponse.isSuccess && result != null) {
onSuccess(result)
} else {
onError(rmResponse.message)
}
}
}
- If other user attempts to link the same sensor to their account it will be removed from the previous user's account.
To save a sensor as 'last used' call updateLastUsedSensorInDatabase this function will save the provided RMSensor in
preferences.
We encourage you to update the last used sensor every time the user connects to a sensor, this will help you to implement other useful features and give a better experience to your users.
fun saveLastUsedSensor(
rmSensor: RMSensor,
onSuccess: () -> Unit,
onError: (String) -> Unit,
) {
rm.updateLastUsedSensorInDatabase(rmSensor) {
if (it.isSuccess) {
onSuccess()
} else {
onError(it.message)
}
}
}
To unlink (delete) a sensor call deleteSensor this function will remove the sensor from the user's profile in Api and
Database.
There's also a deleteSensorFromDatabase function if you only want to get local sensors.
The required RMSensor object must have a non-null uuid, other properties are not necessary.
fun deleteSensor(sensor: RMSensor, onFinish: (Boolean) -> Unit) {
rm.deleteSensor(sensor) { onFinish(it.isSuccess) }
}
Finally, create an instance of the repositories in your.package.name/rm/RMServiceLocator
class RMServiceLocator(context: Context) {
// Other configuration
val sensorRepository by lazy { SensorRepository(rm) }
}
RMSensorScanner
To use the RMSensorScanner class you need to create an instance and implement the RMSensorScannerListener
interface. It can be implemented in an activity or fragment but in order to maintain the state it will be implemented in
a wrapper class SensorScannerImp which will expose the state in StateFlows then, that class will be provided to
a SensorScannerViewModel in the next section.
IMPORTANT:
RMSensorScanneris only for scanning it cannot connect to a sensor, the connection process is done with theRMTrainerclass which is focused on training sessions and Used in the next tutorial.
Got to your.package.name/ui/scanner and create a SensorScannerImp class with a Context and an CoroutineScope as
constructor parameters. This class must implement the RMSensorScannerListener interface.
package com.rookmotion.rooktraining.ui.scanner
import android.bluetooth.le.ScanResult
import android.content.Context
import com.rookmotion.app.sdk.rmsensor.BluetoothAdapterState
import com.rookmotion.app.sdk.rmsensor.RMSensorScannerListener
import com.welie.blessed.BluetoothPeripheral
import com.welie.blessed.ScanFailure
import kotlinx.coroutines.CoroutineScope
class SensorScannerImp(
context: Context,
private val scope: CoroutineScope
) : RMSensorScannerListener {
override fun adapterStateChanged(state: BluetoothAdapterState?) {
TODO("Not yet implemented")
}
override fun newSensor(sensor: BluetoothPeripheral, scanResult: ScanResult) {
TODO("Not yet implemented")
}
override fun newSensorAdded(sensors: MutableList<BluetoothPeripheral>) {
TODO("Not yet implemented")
}
override fun scanFailed(scanFailure: ScanFailure) {
TODO("Not yet implemented")
}
}
Create a RMSensorScanner instance, a discovered map and a connectedMac blank string.
- The
RMSensorScannerwill scan and notify throughRMSensorScannerListenerabout sensors found, errors and the state of the device's bluetooth adapter. discoveredwill store the sensors found in a MAC - BluetoothPeripheral relation to avoid duplicates.connectedMacwill prevent from adding a sensor which is already connected to the discovered map.
val scanner by lazy { RMSensorScanner(context, this) }
private val discovered = mutableMapOf<String, BluetoothPeripheral>()
private var connectedMac = ""
Create 3 StateFlows to manage the adapter, discovered sensors and error states.
private val _adapterState = MutableStateFlow(BluetoothAdapterState.NONE)
val adapterState = _adapterState.asStateFlow()
private val _scannerError = MutableStateFlow<ScanFailure?>(null)
val scannerError get() = _scannerError.asStateFlow()
private val _discoveredSensors = MutableStateFlow<List<BluetoothPeripheral>>(emptyList())
val discoveredSensors get() = _discoveredSensors.asStateFlow()
Create 2 functions to init the connectedMac and to reset the scannerError once the user has seen the message.
fun setConnectedMac(mac: String) {
connectedMac = mac
}
fun resetScannerError() {
scope.launch { _scannerError.emit(null) }
}
Implement the RMSensorScannerListener callbacks
- adapterStateChanged - Called every time the bluetooth is turned off/on (or is in the process of doing so).
- newSensor - Called every time a new sensor is discovered, if the sensor mac (address) is not equal
to
connectedMacand is not duplicated it will be added to thediscoveredmap then the updated map values will be emitted. - newSensorAdded - Called every time a new sensor is discovered, but it returns an updated list, in this case it's not needed, so it will be ignored.
- scanFailed - Called when a scan request made with
startDiscoveryfails there are multiple reason a scan could fail,ScanFailurevalues will be further explained in a future section.
override fun adapterStateChanged(state: BluetoothAdapterState) {
scope.launch { _adapterState.emit(state) }
}
override fun newSensor(sensor: BluetoothPeripheral, scanResult: ScanResult) {
if (connectedMac != sensor.address && !discovered.contains(sensor.address)) {
discovered[sensor.address] = sensor
_discoveredSensors.value = discovered.values.toList()
}
}
override fun newSensorAdded(sensors: MutableList<BluetoothPeripheral>) {
Timber.i("newSensorAdded: $sensors")
}
override fun scanFailed(scanFailure: ScanFailure) {
scope.launch { _scannerError.emit(scanFailure) }
}
Finally, create a onDestroy function to cancel any pending job, this will be called when the SensorScannerActivityis
destroyed.
fun onDestroy() {
scope.cancel()
}
Coding the ViewModels
This section covers one view model:
- SensorScannerViewModel - Used in
SensorScannerActivityto handle all scanner states and to link, save, get and delete sensors.
The file structure should look like below:
your.package.name/
|-- state/
|-- SensorScannerViewModel
Create an SensorScannerViewModel class extending from ViewModel with an SensorScannerImp and a SensorRepository
instance as constructor parameters.
package com.rookmotion.rooktraining.state
import androidx.lifecycle.ViewModel
import com.rookmotion.rooktraining.data.repository.SensorRepository
import com.rookmotion.rooktraining.ui.scanner.SensorScannerImp
class SensorScannerViewModel(
val scannerImp: SensorScannerImp,
private val sensorRepository: SensorRepository
) : ViewModel() {
}
Create 2 livedata objects to hold connectedSensorState and linkSensorState state.
The connectedSensorState will be used to update the UI when a sensor is already connected, so instead of being shown
in the list (it cannot because it's filtered in SensorScannerImp) it will be shown at the top.
private val _connectedSensorState = MutableLiveData<ConnectedSensorState>(ConnectedSensorState.None)
val connectedSensorState: LiveData<ConnectedSensorState> get() = _connectedSensorState
private val _linkSensorState = MutableLiveData<LinkSensorState>()
val linkSensorState: LiveData<LinkSensorState> get() = _linkSensorState
Then add the scanner function calls
fun setConnected(mac: String?, name: String) {
if (mac != null) {
scannerImp.setConnectedMac(mac)
_connectedSensorState.value = ConnectedSensorState.Connected(mac, name)
} else {
_connectedSensorState.value = ConnectedSensorState.None
}
}
fun startScan(fromError: Boolean = false) {
if (fromError) {
scannerImp.resetScannerError()
}
if (scannerImp.scanner.isBluetoothEnabled && !scannerImp.scanner.isDiscovering) {
scannerImp.scanner.startDiscovery()
}
}
fun stopScan() {
if (scannerImp.scanner.isBluetoothEnabled && scannerImp.scanner.isDiscovering) {
scannerImp.scanner.stopDiscovery()
}
}
fun releaseScannerResources() {
scannerImp.onDestroy()
scannerImp.scanner.onDestroy()
}
IMPORTANT:
- Before starting a scan is recommended to verify that other scans aren't in progress with
scanner.isDiscovering. - Before starting or stopping a scan you MUST make sure the bluetooth is enabled with
scanner.isBluetoothEnabledotherwise your app will crash. - You MUST call
scanner.onDestroy()only when you don't need the scanner anymore, once this function is called the currentRMSensorScannerinstance will no longer be useful.
Then call the repository's functions
fun linkToSensor(peripheral: BluetoothPeripheral) {
sensorRepository.saveSensor(
peripheral = peripheral,
onSuccess = { saveLastUsedSensor(it) },
onError = {
_linkSensorState.value = LinkSensorState(
success = false,
mac = peripheral.address,
error = it
)
}
)
}
private fun saveLastUsedSensor(rmSensor: RMSensor) {
sensorRepository.saveLastUsedSensor(
rmSensor = rmSensor,
onSuccess = {
_linkSensorState.value = LinkSensorState(success = true, mac = rmSensor.sensorMac)
},
onError = {
_linkSensorState.value = LinkSensorState(
success = false,
mac = rmSensor.sensorMac,
error = "Database error"
)
}
)
}
- Once the user clicks on a sensor it will be linked and then saved as 'last used'.
The connectedSensorState and linkSensorState use sealed and a data class like the following:
sealed class ConnectedSensorState {
object None : ConnectedSensorState()
class Connected(val mac: String, val name: String) : ConnectedSensorState()
}
data class LinkSensorState(
val linking: Boolean = false,
val success: Boolean = false,
val mac: String? = null,
val error: String? = null
)
- The
linkToSensorwill return an error when the user has no internet access, that will prevent the user from connecting to a sensor, to prevent that case the MAC will always be returned, so even iflinkToSensororsaveLastUsedSensorfail the user will still be able to connect their sensor.
This ViewModel has dependencies which relies on Context, so a new Factory is needed, create an
RMApplicationViewModelFactory class implementing from ViewModelProvider.Factory with an RookTrainingApplication
instance as a constructor parameter.
package com.rookmotion.rooktraining.state
import androidx.lifecycle.ViewModelProvider
import com.rookmotion.rooktraining.RookTrainingApplication
@Suppress("UNCHECKED_CAST")
class RMApplicationViewModelFactory(
private val application: RookTrainingApplication,
) : ViewModelProvider.Factory {
}
Then override create adding a case for SensorScannerViewModel.
override fun <T : ViewModel> create(modelClass: Class<T>): T {
if (modelClass.isAssignableFrom(SensorScannerViewModel::class.java)) {
return SensorScannerViewModel(
scannerImp = SensorScannerImp(
context = application.applicationContext,
scope = CoroutineScope(SupervisorJob() + Dispatchers.Default)
),
sensorRepository = application.rmServiceLocator.sensorRepository
) as T
}
throw IllegalArgumentException("Unknown ViewModel class")
}
This factory will be used in future tutorials for features that depend on Context.
Integrating ViewModel and UI
HomeActivity
In the initActions function add a call to startActivity.
private fun initActions() {
// Other buttons
binding.sensorScanner.setOnClickListener {
startActivity(Intent(this, SensorScannerActivity::class.java))
}
}
The SensorScannerActivity requires bluetooth and location modify the enablePermissionsScreens
and disablePermissionsScreens functions to disable sensorScanner button when the app has no permissions.
private fun enablePermissionsScreens() {
// Other config
binding.sensorScanner.isEnabled = true
}
private fun disablePermissionsScreens() {
// Other config
binding.sensorScanner.isEnabled = false
}
SensorScannerActivity
Create an SensorScannerViewModel and a BLPeripheralAdapter instance
class SensorScannerActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private lateinit var blPeripheralAdapter: BLPeripheralAdapter
private val scannerViewModel by viewModels<SensorScannerViewModel> {
RMApplicationViewModelFactory(application as RookTrainingApplication)
}
}
The BLPeripheralAdapter will be initialized in onCreate
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
blPeripheralAdapter = BLPeripheralAdapter { scannerViewModel.linkToSensor(it) }
initExtras()
initState()
initUI()
}
Override onDestroy to stop scan and release resources when the activity is destroyed.
override fun onDestroy() {
if (!isChangingConfigurations) {
scannerViewModel.stopScan()
scannerViewModel.releaseScannerResources()
}
super.onDestroy()
}
Create the initExtras function to get the connected sensor.
private fun initExtras() {
val mac = intent?.extras?.getString(ScannerKeys.SENSOR_CONNECTED_MAC)?.uppercase()
val name = intent?.extras?.getString(ScannerKeys.SENSOR_CONNECTED_NAME)
scannerViewModel.setConnected(mac, name ?: getString(R.string.unknown_sensor))
}
Consume the connectedSensorState livedata and implement all cases:
- None - The activity that started
SensorScannerActivitydid not provide the connected keys so, no sensor it's connected, theconnectedSensorview is removed. - Connected - A connected sensor was provided show
connectedSensorview with the connected sensor's name.
private fun initState() {
scannerViewModel.connectedSensorState.observe(this) {
when (it) {
SensorScannerViewModel.ConnectedSensorState.None -> {
binding.connectedSensor.isVisible = false
}
is SensorScannerViewModel.ConnectedSensorState.Connected -> {
binding.connectedSensor.text = getString(
R.string.connected_to_placeholder,
it.name
)
binding.connectedSensor.isVisible = true
}
}
}
}
- In the individual training tutorial the current connected sensor will be provided.
Consume the linkSensorState livedata and implement all cases:
- linking - When true show progress view, otherwise show the items list.
- success - When true show a toast.
- mac - When not-null call
selectAndExit. - error - When not-null, show a toast.
private fun initState() {
// Other state
scannerViewModel.linkSensorState.observe(this) {
if (it.linking) {
showProgress()
} else {
showItems()
}
if (it.success) {
toastShort(getString(R.string.sensor_linked))
}
if (it.mac != null) {
selectAndExit(it.mac)
}
if (it.error != null) {
toastLong(it.error)
}
}
}
Consume the discoveredSensors stateflow and implement all cases:
- it - If not empty submit the list to
blPeripheralAdapterand show items list, otherwise show progress
private fun initState() {
// Other state
lifecycleScope.launchWhenResumed {
scannerViewModel.scannerImp.discoveredSensors.collect {
if (it.isNotEmpty()) {
blPeripheralAdapter.submitList(it)
showItems()
} else {
showProgress()
}
}
}
}
Consume the scannerError stateflow and implement all cases:
- it - If not-null show an error.
private fun initState() {
// Other state
lifecycleScope.launchWhenResumed {
scannerViewModel.scannerImp.scannerError.collect {
if (it != null) {
showError(it)
}
}
}
}
Create the initUI function to configure the data RecyclerView.
private fun initUI() {
binding.data.setHasFixedSize(true)
binding.data.adapter = blPeripheralAdapter
}
Create the selectAndExit function to finish the activity with the selected sensor MAC.
private fun selectAndExit(mac: String) {
val intent = Intent().apply {
putExtra(ScannerKeys.SENSOR_SELECTED, mac)
}
setResult(Activity.RESULT_OK, intent)
finish()
}
Create showProgress and showItems functions.
private fun showProgress() {
binding.progress.root.isVisible = true
binding.data.isVisible = false
}
private fun showItems() {
binding.progress.root.isVisible = false
binding.data.isVisible = true
}
Finally, the showError will display a message for every case of error, and a Retry button.
When the user clicks on retry it will make a call to startScan with fromError on true, this will start a new scan
and also reset the scannerError stateflow to prevent the message from appearing again.
private fun showError(scanFailure: ScanFailure) {
val messageRes = when (scanFailure) {
ScanFailure.APPLICATION_REGISTRATION_FAILED,
ScanFailure.INTERNAL_ERROR,
ScanFailure.UNKNOWN -> R.string.error_internal_bluetooth
ScanFailure.ALREADY_STARTED -> R.string.error_already_scanning
ScanFailure.FEATURE_UNSUPPORTED -> R.string.error_not_supported
ScanFailure.OUT_OF_HARDWARE_RESOURCES -> R.string.error_no_resources
ScanFailure.SCANNING_TOO_FREQUENTLY -> R.string.error_too_much_scans
}
binding.root.snackLong(getString(messageRes), getString(R.string.retry)) {
scannerViewModel.startScan(fromError = true)
}
}
Running the app
Wrapping up
At the end of this tutorial your app should be able to:
Show a sensors list.
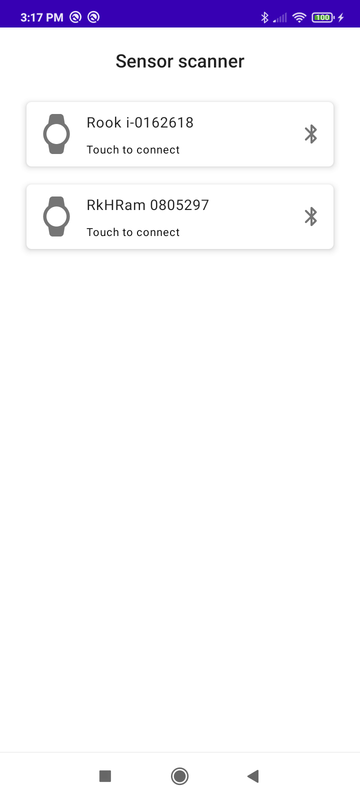
Link a sensor to a user.
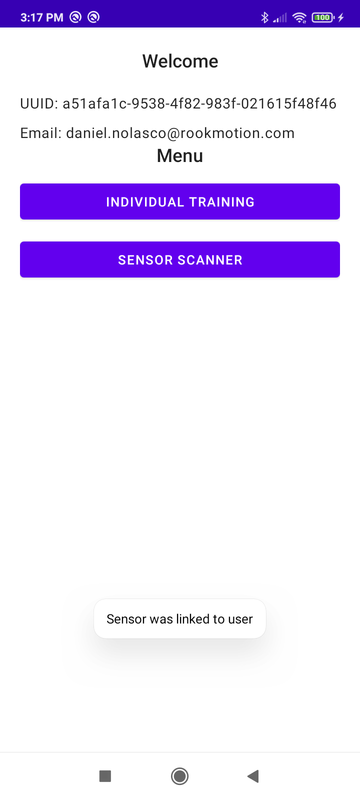
- Turn off your Wi-Fi, data and repeat, an error toast should appear but the mac is still being returned.
If you want to test the connectedSensorState modify the intent that starts the SensorScannerActivity like below:
binding.sensorScanner.setOnClickListener {
startActivity(Intent(this, SensorScannerActivity::class.java).apply {
putExtra(
ScannerKeys.SENSOR_CONNECTED_MAC,
"FB:6B:F4:5C:4E:4E"
) // Replace this with the MAC of one of your sensors.
putExtra(ScannerKeys.SENSOR_CONNECTED_NAME, "RkHRam 0805297")
})
}
Then restart the app, the sensors list won't include the 'connected sensor', it will be displayed at the top.

- Don't forget to revert this last change.
Next steps
Congratulations! You successfully retrieved a list of training types, go to the next tutorial to learn about Individual training sessions.